Science Class 7 Chapter 10 Question Answer Life Processes in Animals
Life Processes in Animals Class 7 Question Answer (InText)
Question 1.
How does sunlight contribute in the production of starch in plants? (Page 141)
Answer:
Sunlight is important for photosynthesis, the process by which plants make food. The chlorophyll present in the leaves helps in capturing sunlight. In the process of photosynthesis, plants use the absorbed sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make
glucose. This glucose is later stored in the plant as starch.

Question 2.
Which gas from the air is essential in the process of food preparation in plants? (Page 143)
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is essential for the process of food preparation in plants.
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Question Answer Life Processes in Plants (Exercise)
Let Us Enhance Our Learning
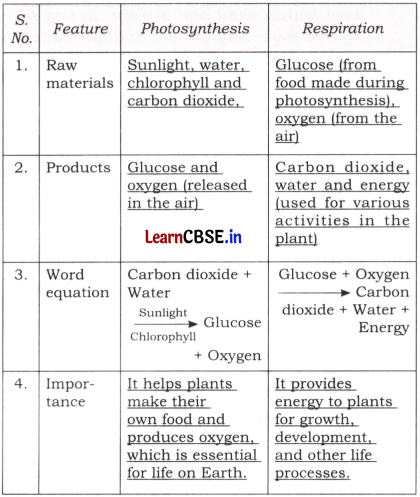
Question 1.
Complete the following table.
Answer:
Question 2.
Imagine a situation where all the organisms that carry out photosynthesis on the earth have disappeared. What would be the impact of this on living organisms?
Answer:
If all organisms that cany out photosynthesis disappeared, there would be no production of oxygen and food for other living organisms. This would disrupt the food chain, as plants provide food for herbivores and oxygen for respiration. Without plants, life on Earth would not be sustained.
Question 3.
A potato slice shows the presence of starch with iodine solution. Where does the starch in potatoes come from? Where is the food synthesised in the plant, and how does it reach the potato?
Answer:
The starch in potatoes comes from the glucose produced in the leaves during photosynthesis. Photosynthesis occurs in the leaves, where food is synthesised in the form of glucose. This glucose is then transported through the plant to the potato, where it is stored in the form of starch.
Question 4.
Does the broad and flat structure of leaves make plants more efficient for photosynthesis? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Yes, the broad and flat structure of leaves makes plants more efficient for photosynthesis. This shape increases the surface area, allowing more sunlight to be absorbed by the chlorophyll present in the leaves. It also helps in the exchange of gases through the stomata, thus enhancing the process of photosynthesis.

Question 5.
X is broken down using Y to release carbon dioxide, Z, and energy.
X + Y → Carbon dioxide + Z + Energy
X, Y, and Z are three different components of the process. What do X, Y, and Z stand for?
Answer:
X – Glucose
Y – Oxygen
Z – Water
Question 6.
Krishna set-up an experiment with two potted plants of same size and placed one of them in sunlight and the other in a dark room, as shown in Fig. 10.10.
Fig. Experimental pots, (a) Sunlight (b) Complete dark
Answer the following questions.
(i) What idea might she be testing through this experiment?
Answer:
Through this experiment, she is testing whether sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis in plants or not.
(ii) What are the visible differences in plants in both the conditions?
Answer:
The plant kept in sunlight looks healthy and green as it performs photosynthesis while the plant kept in the dark room looks weak, pale, and yellowish because it cannot perform photosynthesis properly.
(iii) According to you, leaves of which plants confirm the iodine test for the presence of starch?
Answer:
The leaves of the plant kept in sunlight will confirm the iodine test for starch.
Question 7.
Vani believes that ‘carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis’. She puts an experimental set-up, as shown in Fig. 10.11, to collect evidence to support or reject her idea.
Fig. A potted plant with sufficient water is placed under the prescribed conditions.
(a) Sunlight with carbon dioxide
(b) Sunlight without carbon dioxide
(a) Dark with
(b) Dark without carbon dioxide carbon dioxide
Answer the following questions.
(i) In which plant(s) in the above set-up(s) will starch be formed?
Answer:
Only in plant kept in sunlight with carbon dioxide, starch will be formed.
(ii) In which plant(s) in the above set-up(s) will starch not be formed?
Answer:
In all plants except the plant kept in sunlight with carbon dioxide.
(iii) In which plant(s) in the above set-up(s) will oxygen be generated?
Answer: Oxygen will be generated in a plant kept in sunlight with carbon dioxide.
(iv) In which plant(s) in the above set-up(s) will oxygen not be generated?
Answer:
Except for the plant kept in sunlight with carbon dioxide, oxygen will not be generated in any of the other plants.
Question 8.
Ananya took four test tubes and filled three- fourth of each test tube with water. She labelled them A, B, C, and D (Fig. 10.12). In test tube A, she kept a snail; in test tube B, she kept a water plant; in test tube C, she kept both a snail and a plant. In test tube D, she kept only water. Ananya added a carbon dioxide indicator to all the test tubes. She recorded the initial colour of water and observed if there are any colour changes in the test tubes after 2-3 hours. What do you think she wants to find out? How will she know if she is correct?
Fig. Experimental set-up
Answer:
Ananya wants to find out how plants and animals affect the amount of carbon dioxide in water. She is testing the role of respiration and photosynthesis. The carbon dioxide indicator changes colour depending on how much carbon dioxide is present in the water. Ananya will know she is correct by observing the colour changes in the carbon dioxide indicator in each test tube:
- Test Tube A (Snail only): The indicator will turn yellow/orange, showing increased carbon dioxide due to the snail’s respiration.
- Test Tube B (Plant only): The indicator will turn blue/purple, showing decreased carbon dioxide because the plant uses it during photosynthesis.
- Test Tube C (Snail + Plant): The colour may stay neutral or slightly blue, showing a balance as the snail gives out carbon dioxide and the plant uses it.
- Test Tube D (Only water): No colour change, as there is no living organism to add or remove carbon dioxide.

Question 9.
Design an experiment to observe if water transportation in plants is quicker in warm or cold conditions.
Answer:
To test whether water transportation in plants is quicker in warm or cold conditions, take two identical potted plants. Place one plant in a warm location (near a heater or sunny spot) and the other plant in a cool place (like in the shade). Add a few drops of food colouring to the water and water both plants. After a few hours, observe the movement of the coloured water up the stem and into the leaves. The plant in the warm conditions will show faster movement of the coloured water, as higher temperatures increase the rate of evaporation and water transportation.
Question 10.
Photosynthesis and respiration are essential to maintain balance in nature. Discuss.
Answer:
Photosynthesis and respiration help maintain the balance of gases in nature. During photosynthesis, plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food and release oxygen. In respiration, plants and animals use oxygen to break down food for energy, releasing carbon dioxide. This exchange of gases keeps oxygen and carbon dioxide levels balanced, supporting life on Earth.
Class 7 Life Processes in Animals Question Answer (Activities)
Activity 10.1: Let Us Test Some Explanations (Pages 138-139)
Fig. Experimental set-up to understand the role of sunlight and water in plant growth
(a) Pot A kept in direct sunlight, with water
(b) Pot B kept in direct sunlight, without water
(c) Pot C kept in dark with water
Table 10.1: Effects of sunlight and water on plant growth
| Pots kept under different conditions | Availability of | Height of plant (cm) | Number of leaves | Colour of Leaves (Green/ Yellow) |
| Sunlight | Water | Day 1 | After 2 Weeks | Day 1 | After 2 Weeks |
| Pot A: In direct sunlight, with water | Yes | Yes | Same | Taller plant | Same | More green leaves | Green leaves |
| Pot B: In direct sunlight, without water | Yes | No | Same | Possibly | Same | Less than Pot A | Yellow leaves |
| Pot C: In the dark, with water | No | No | Same | wilted | Same | Least | Yellow leaves |
Observation and Conclusion: The following points can be noted:
(i) What differences did you observe between the plants in the three pots?
Answer:
The plants in the three pots showed noticeable differences after two weeks.
Pot A, which received both sunlight and water, grew the tallest, had the most leaves, and stayed green, showing healthy development.
Pot B, with sunlight but no water, showed very little growth, fewer leaves, and yellowing due to dehydration.
Pot C, kept in the dark but watered, exhibited limited growth, with slightly pale yellow leaves and fewer new leaves, indicating that light is essential for healthy, green plants.
(ii) Which pot has the plant with the maximum growth?
Answer:
Pot A
(iii) Which pot has the plant with the least growth?
Answer:
Pot C
Activity 10.2: Let Us Check (Demonstration Activity) (Pages 140-141)
Fig. Starch test in a leaf, (a) Boiling set-up (b) Iodine test
Observation and Conclusion: If the colour of the leaf changes to blue-black, we can conclude that starch is present in the leaf.
Activity 10.3: Let Us Check (Pages 141-142)
Table 10.2: Presence of starch in green and non-green parts of the leaves of plants

Observation and Conclusion:
• Only the green parts of the leaf can perform photosynthesis and make starch due to the presence of chlorophyll.
• Sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis to occur and for starch to be produced in leaves.
Activity 10.4: Let us Experiment (Demonstration Activity) (Pages 143-144)
| Part of the leaf | Availability of | Starch present (Yes/No) |
| Water | Sunlight | Chlorophyll | Carbon dioxide |
| Part of the leaf inside the bottle | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Part of the leaf outside the bottle | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Fig. Testing the role of chlorophyll and air, (a) The set-up (b) Iodine test on the leaf
Observation and Conclusion:
• The part of the leaf that was inside the bottle with caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) did not turn blue-black after the iodine test. This shows that no starch was produced in that part because caustic soda absorbs carbon dioxide, which is needed for photosynthesis.
• The part of the leaf that was outside the bottle turned blue-black, showing that starch was produced because that part had access to carbon dioxide and could perform photosynthesis. This experiment proves that carbon dioxide is necessary for plants to prepare starch.
Activity 10.5: Let Us Explore (Page 145)
Fig. Activity showing the release of oxygen during photosynthesis
(i) What difference do you observe in the two set¬ups?
Answer:
In set-up A (kept in sunlight), we observe bubbles on the inverted test tube. While in set¬up B (kept in the dark), no bubbles are seen.
(ii) Do you observe air bubbles emerging in the inverted test tube in set-up A?
Answer:
Yes, air bubbles are seen rising and collecting in the inverted test tube in set-up A.
(iii) The gas produced in this set-up caused bubbles to emerge and get accumulated in the inverted test tube. Which gas is this?
Answer:
The gas produced is oxygen, which is released during photosynthesis.
Observation and Conclusion:
• When a test tube is taken off the set-up and a lit matchstick is inserted into the tube, it produces an intense flame, which confirms that oxygen gas is released during the process of photosynthesis.

Activity 10.6: Let Us Examine (demonstration activity) (Page 147)
Observation
(i) What do you observe?
Answer:
Tiny pores on the peel of the leaf.
(ii) Do you notice tiny pores on the peel?
Answer:
Yes
Conclusion:
• These tiny pores are stomata. They are prsent on the surface of leaves, help in the exchange of gases.
Fig. Stomata on the lower surface of a rhoeo leaf
Activity 10.7: Let Us Experiment (Page 148)
(a) With water (b) With coloured water plant twigs placed in water with different treatments
Fig. 10.7: Experiment to check for water transportation in plants
Observation and Conclusion:
• This experiment shows that water and minerals are transported through the xylem in plants. Xylem is thin, tube-like structure found in the stem, branches, and leaves, carrying water and minerals from the roots to all parts of the plant.
Activity 10.8: Let Us Find Out (Demonstration Activity) (Page 149)
Fig. Experiment to check for water transportation in plants
(a) With water
(b) With coloured water, plant twigs placed in water with different treatments
(c) With water
(d) With coloured water, plant twigs after one day
(e) Enlarged view of cut end of the twig
Observation and Conclusion:
• This experiment shows that water and minerals are transported through the xylem in plants. Xylem is thin, tube-like structure found in the stem, branches, and leaves, carrying water and minerals from the roots to all parts of the plant.
Activity 10.8: Let Us Find Out (Demonstration Activity) (Page 149)
Fig. Set-up to test respiration in plants
(i) Does the lime water turn milky in both the test tubes?
Answer:
The lime water turn milky only in the test tube connected to the flask.
(ii) Why does the lime water turn milky in the test tube connected to the flask?
Answer:
Lime water turns milky due to the presence of carbon dioxide. This carbon dioxide is produced by the seeds during respiration.
Observation and Conclusion: Plants also respire like us and release carbon dioxide.
![]()

![]()



![]()





![]()









0 Comments