NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Ganita Prakash Chapter 7 Fractions
7.1 Fractional Units and Equal Shares Figure it Out (Page No. 152 – 153)
Fill in the blanks with fractions.
Question 1.
Three guavas together weigh 1 kg. If they are roughly of the same size, each guava will roughly weigh ____kg.
Solution:
13Question 2.
A wholesale merchant packed 1 kg of rice in four packets of equal weight. The weight of each packet is _________ kg.
Solution:
14Question 3.
Four friends ordered 3 glasses of sugarcane juice and shared it equally. Each one drank ____________ glass of sugarcane juice.
Solution:
34As total quantity is 3 which is to be divided into four equal parts. So, the required fraction is
34.
Question 4.
The bis fish weighs
12 kg. The small one weighs
14 kg. Together they weigh ____ kg.
Solution:
Given the weighs of big fish =
12kg and the weighs of small fish =
14kg
Total weight of both fish =
12+
14=
2+14 kg
=
34 kg
Question 5.
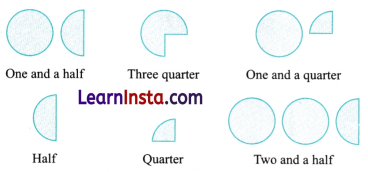
Arrange these fraction words in order of size from the smallest to the biggest in the empty box below: One and a half, three quarters, one and a quarter, half, quarter, two and a half.
Solution:
∴ The fractions from smallest to the biggest are as follows: quarter, half, three quarters one and a quarter, one and a half, two and a half.

7.2 Fractional Units as Parts of a Whole Figure it Out (Page No. 155)
Question 1.
The figure below shows different fractional units of a whole chikki. How much of a whole chikki is each piece?
Solution:
(a)
Total no. of pieces formed of given size = 12
Required fraction =
112(b)
Total no. of pieces formed of given size = 4
Required fraction =
14(c)
Total no. of pieces formed of given size = 8
Required fraction =
18(d)
Total no. of pieces formed of given size = 6
Required fraction =
16(e)
Total no. of pieces formed of given size = 8
Required fraction =
18(f)
Total no. of pieces formed of given size = 8
Required fraction =
18
(g)
Total no. of pieces formed of given size = 24
Required fraction =
124(h)
Total no. of pieces formed of given size = 12
Required fraction =
1127.3 Measuring Using Fractional Units Figure it Out (Page No. 158)
Question 1.
Continue this table of
12 for 2 more steps.
Solution:
Question 2.
Can you create a similar table for
14 ?
Solution:
Yes.

Question 3.
Make
13 using a paper strip. Can you use this to also make
16?
Solution:
Take a strip of paper.
Fold the strip into three equal parts and then open up.
Yes, we can also make
16 using a paper strip by folding 6 again the above strip.
Question 4.
Draw a picture and write an addition statement as above to show:
(a) 5 times
14 of a roti
Solution:
5 times
14 of a roti
=
14+
14+
14+
14+
14(b) 9 times
14 of a roti
Solution:
9 times
14 of a roti
=
14+
14+
14+
14+
14+
14+
14+
14+
14
Question 5.
Match each fractional unit with the correct picture:
Solution:
7.4 Marking Fraction Lengths on the Number Line Figure it Out (Page No. 160)
Question 1.
On a number line, draw lines of length
110,
310, and
45.
Solution:
Divide the unit into 10 equal parts and point A represents
110.
Divide a unit into 10 equal parts and point B represents
310.
Divide a unit into 5 equal parts and point C represents
45.
Question 2.
Write five more fractions of your choice and mark them on the number line.
Solution:
The fractions are
35,
13,
57,
25 and
18.
Their number line representations are:
Question 3.
How many fractions lie between 0 and 1? Think, discuss with your classmates, and write your answer.
Solution:
There are an infinite number of fractions between 0 and 1.
Example:
35,
45,
71012 etc.
Question 4.
What is the length of the pink line and black line shown below? The distance between 0 and 1 is 1 unit long, and it is divided into two equal parts. The length of each part is
12. So the pink line is y units long. Write the fraction that gives the length of the black line in the box.
Solution:
Length of black line is
12;
Length of black line is
12 +
12 +
12Fraction that gives length of black line =
32Question 5.
Write the fraction that gives the lengths of the black lines in the respective boxes.
Solution:
Intext Questions
Question 1.
Here, the fractional unit is dividing a length of 1 unit into three equal parts. Write the fraction that gives the length of the pink line in the box or in your notebook. (Page 159)
Solution:
Here number line OR is divided into three equal parts OP, PQ and QR.
Hence length of pink line = OP + PQ =
13+
13=
23Question 2.
Here, a unit is divided into 5 equal parts. Write the fraction that gives the length of the pink lines in the respective boxes or in your notebook.
Solution:
Here number line OT = 1 unit is divided into five equal parts OP, PQ, QR, RS and ST.
Hence length of pink line OQ = OP + PQ =
15+
15=
25Now, length of pink line OS = OP + PQ + QR + RS =
15+
15+
15+
15=
45Hence, OQ =
25 OS =
45
Question 3.
Now, a unit is divided into 8 equal parts. Write the appropriate fractions in your notebook Solution:Here number line OH is divided into 8 equal parts OA, AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG and GH.
Solution:
Also, OA =
18, OB =
28, OC =
38, OH =
88 = 1
7.5 Mixed Fractions Figure it Out (Page No. 162)
Question 1.
How many whole units are there in
72?
Solution:
72=
12+
12+
12+
12+
12+
12+
12=3+
12So, there are 3 whole units in
72.
Question 2.
How many whole units are there in
43 and in
73?
Solution:
43=
13+
13+
13+
13=1+
13So, there are 1 whole unit in
43.
73=
13+
13+
13+
13+
13+
13+
13=2+
13So, there are 2 whole units in
73.
7.5 Mixed Fractions Figure it Out (Page No. 162)
Question 1.
Figure out the number of whole units in each of the following fractions:
(a)
83(b)
115(c)
94Solution:
(a) 2
(b) 2
(c) 2
Question 2.
Can all fractions greater than 1 be written as such mixed numbers?
Solution:
Yes.
Question 3.
Write the following fractions as mixed fractions (e.g.
92 = 4
12)
(a)
92Solution:
= 4
12(b)
95Solution:
= 1
45(c)
2119Solution:
= 1
219(d)
479Solution:
= 5
29(e)
1211Solution:
= 1
111(f)
196Solution:
= 3
167.5 Mixed Fractions Figure it Out (Page No. 163)
Question 1.
Write the following mixed numbers as fractions:
(a) 3
14(b) 7
23(c) 9
49(d) 3
16(e) 2
311(f) 3
910Solution:
7.6 Equivalent Fractions Figure it Out 7.7 Simplest form of a Fraction Figure it Out (Page No. 165)
Question 1.
Are
36,
48,
510 equivalent fractions? Why?
Solution:
Here, simplest form of
36=
3÷36÷3=
12 [HCF of 3 and 6 is 3]
and simplest form of
48 is
4÷48÷4=
12 [HCF of 4 and 8 is 4]
and simplest form of
510 is
5÷510÷5=
12 [HCF of 5 and 10 is 5]
Hence,
36,
48,
510 are equivalent fractions.
Question 2.
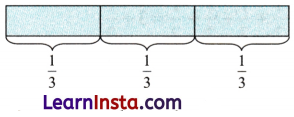
Write two equivalent fractions for
26.
Solution:
From the fractional wall we can choose any two fractions that denote the same length as
26⋅
26=
13=
39
Question 3.
46 = ___________ = ___________ = ___________ = ___________________
(Write as many as you can)
Solution:
Here,
Intext Questions
Answer the following questions after looking at the fraction wall: [Page 164]
Question 1.
Are the lengths
12 and
36 equal?
Solution:
Yes, here lengths
12 and
36 =
12Lengths are equal.
Question 2.
Are
23 and
46 equivalent fractions? Why?
Solution:
Yes, lengths
23 and
46 =
13 are equivalent fraction, as they have same length.
Question 3.
How many pieces of length
16 will make a length of
12?
Solution:
Total no.of pieces =
1216=
12×
61=
62 = 3
Hence three pieces of length
16 will make a length of
12Question 4.
How many pieces of length
16 will make a length of
13?
Solution:
Total no. of pieces =
1316=
13×
61=
63 = 2
Hence two pieces of length
16 will make a length of
13.
7.7 Simplest form of a Fraction Figure it Out (Page No. 166)
Question 1.
Three rotis are shared equally by four children, show the division in the picture and write a fraction of how much each child gets. Also, write the corresponding division facts, addition facts, and, multiplication facts.
The fraction of roti each child gets is ___________
Division fact:
Addition fact:
Multiplication fact:
Compare your picture and answer with your classmates!
Solution:
One roti is shared as shown in the figure below:
The four shares must be equal to each other!
Similar distribution will be done for the second and third roti also.
So, each child will get
34 a piece of roti.
The division fact is 3 ÷ 4 =
34The addition fact is 3 =
34+
34+
34+
34The multiplication fact is 3 = 4 ×
34Question 2.
Draw a picture to show how much each child gets when 2 rotis are shared equally by 4 children. Also, write the corresponding division facts, addition facts, and multiplication facts.
Solution:
One roti is shared as shown in the figure below:
The four shares must be equal to each other!
A similar distribution will be done for the second roti also.
So, each child will get
14 part from a rod.
So, the total fraction of roti received by each child from 2 rotis =
24 =
12The division fact is 2 ÷ 4 =
24The addition fact is =
24+
24+
24+
24The multiplication fact is 2 = 4 ×
24
Question 3.
Anil was in a group where 2 cakes were divided equally among 5 children. How much cake would Anil get?
Solution:
Anil would get
25 part of the cake.
7.7 Simplest form of a Fraction Figure it Out (Page No. 168 – 169)
Question 1.
Find the missing numbers:
(a) 5 glasses of juice shared equally among 4 friends is the same as ____________ glasses of juice shared equally among 8 friends. So,
54 =
?8.
(b) 4 kg of potatoes divided equally in 3 bags is the same as 12 kgs of potatoes divided equally in ____________ bags. So,
43 =
12?.
(c) 7 rods divided among 5 children is the same as rods divided among children. So,
75 = ____________
Solution:
(a) Here, the amount of juice each friend gets when 5 glasses are shared among 4 friends =
number of glasses number of friends =
54Now to determine how many glasses of juice would be needed to give each of the 8 friends the same amount = 8 ×
54= 10 glasses
So, 10 glasses of juice shared equally among 8 friends is the same as 5 glasses of juice shared equally among 4 friends.
∴
54=
108(b) Here 4 kg of potatoes divided equally in 3 bags then amount of potatoes per bag =
4 kg3 bags =
43 kg per bag
Let x is the number of bags for 12 kg of potatoes, where each bag has the same amount of potatoes then
12 kgx bags =
43 kg per bag
⇒ 12 × 3 = 4 × x
⇒ 36 = 4x
⇒ x =
364⇒ x = 9
∴
43=
129(c) Dividing 7 rotis among 4 children gives 7 each child =
75 of a roti. We can find an
equivalent fraction by multiplying both the numerator and the denominator by the same number. For example, multiplying both by 2.
7×25×2=
1410So, 7 rotis divided among 5 children is the same as 14 rotis divided among 10 children
∴
75=
1410Intext Questions
Question 1.
Find equivalent fractions for the given pairs of fractions such that the fractional units are the same. (Page 172)
(a)
72 and
35Solution:
Given fractions are
72 and
35Here, the denominators are 2 and 5.
And least common multiple of 2 and 5 is 10.
Hence for both fractions let’s have same denominator of 10.
Now for
72 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 5.
72=
7×52×5=
3510And for
35 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 2, we get,
3×25×2=
610Hence, the equivalent fractions with the same denominator are:
3510 and
610(b)
83 and
56Solution:
Given fractions are
83 and
56Here, the denominators are 3 and 6.
And least common multiple of 3 and 6 is 6.
Now for
83 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 2.
83=
8×23×2=
16656 already have a denominator 6.
Hence, the equivalent fractions with the same denominator are:
166 and
56(c)
34 and
35Solution:
Given fractions are
34 and
35Here, the denominators are 4 and 5.
And least common multiple of 4 and 5 is 20.
Now for
34 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 5.
34=
3×54×5=
1520And for
35 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 4, we get
35=
3×45×4=
1220So, the equivalent fractions with the same denominator are:
1520 and
1220(d)
67 and
85Solution:
Given fractions are
67 and
85Here, the denominators are 7 and 5.
And least common multiple of 7 and 5 is 35.
Now for
67 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 5.
67=
6×57×5=
3035And for
85 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 7, we get
85=
8×75×7=
5635So, the equivalent fractions with the same denominator are:
3035 and
5635(e)
94 and
52Solution:
Given fractions are
94 and
52Here, the denominators are 4 and 2.
And least common multiple of 4 and 2 is 4.
Now for
52 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 2.
52=
5×22×2=
104and
94 already have a denominator 4
So, the equivalent fractions with the same denominator are:
94 and
104(f)
110 and
29Solution:
Given fractions are and
110 and
29Here, the denominators are 10 and 9.
And least common multiple of 10 and 9 is 90.
Now for
110 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 9.
110=
1×910×9=
990And for 2 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 10, we get
29=
2×109×10=
2090So, the equivalent fractions with the same denominator are:’
990 and
2090(g)
83 and
114Solution:
Given fractions are
83 and
114Here, the denominators are 3 and 4.
And least common multiple of 3 and 4 is 12.
Now for
83 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 4.
83=
8×43×4=
3212And for
114 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 3, we get
114=
11×34×3=
3312So, the equivalent fractions with the same denominator are:
3212 and
3312(h)
136 and
19Solution:
Given fractions are
136 and
19Here, the denominators are 6 and 9.
And least common multiple of 6 and 9 is 18.
Now for
136 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 3.
136=
13×36×3=
3918And for
19 multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 2, we get
19=
1×29×2=
218So, the equivalent fractions with the same denominator are:
3918 and
218
7.7 Simplest form of a Fraction Figure it Out (Page No. 173)
Question 1.
Express the following fractions in lowest terms:
(a)
1751Solution:
13(b)
64144Solution:
49(c)
126147Solution:
67(d)
525112Solution:
75167.8 Comparing Fractions Figure it Out (Page No. 174)
Question 1.
Compare the following fractions and justify your answers:
(a)
83,
52(b)
49,
37(c)
710,
914(d)
125,
85(e)
94,
52Solution:
Question 2.
Write following fractions ascending order.
(a)
710,
1115,
25Solution:
The given fractions are
710,
1115,
25Let us find LCM of denominator 10, 15, 5
∴ LCM of 10, 15 and 5 = 2 × 3 × 5 = 30
Now let us make denominator of each fractions as LCM
Hence given fractions in ascending order are:
25,
710115(b)
1924,
56,
712Solution:
The given fractions are
1924,
56,
712Here LCM of 24, 6, 12 is 24.
On arranging in ascending Order, we get
1424,
1924,
2024⇒
712,
1924,
56
Question 3.
Write the following fractions in descending order.
(a)
2516,
78,
134,
1732Solution:
(b)
34,
125,
712,
54Solution:
7.9 Relation to Number Sequences Figure it Out (Page No. 179)
Question 1.
Add the following fractions using Brahmagupta’s method:
(a)
27+
57+
67Solution:
27+
57+
67=
2+5+67=
137=1
67
(b)
34+
13Solution:
34+
13=
34×
33+
13×
44=
912+
412=
9+412=
1312= 1
112(c)
23+
56Solution:
23+
56=
23×
22+
5646+
56=
96=
32= 1
12(d)
23+
27Solution:
23+
27=
23×
77+
27×
33=
1421+
621=
2021(e)
34+
13+
15Solution:
4560+
2060+
1260=
7760= 1
1760(f)
23+
45Solution:
1015+
1215=
2215= 1
715(g)
45+
23Solution:
1215+
1015=
2215= 1
715(h)
35+
58Solution:
2440+
2540=
4940=
940(i)
92+
54Solution:
184+
54=
234= 5
34(j)
83+
27Solution:
5621+
621=
6221= 2
2021(k)
34+
13+
15Solution:
4560+
2060+
1260=
7760= 1
1760(l)
23+
45+
37Solution:
70105+
84105+
45105=
199105= 1
94105
(m)
92+
54+
76Solution:
5412+
1512+
1412=
8312=
1112Question 2.
Rahim mixes
23 liters of yellow paint with
34 liters of blue paint to make green paint What is the volume of green paint he has made?
Solution:
Quantity of yellow paint added =
23 litres
Quantity of blue paint added =
34 litres
Total quantity of green paint made =
23 +
34LCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
23=
23×
44=
81234=
34×
33=
912812+
912=
8+912=
1712So, the total quantity of paint made is
1712 liters.

Question 3.
Geeta bought
25 meter of lace and Shamim bought
34 meter of the same lace to put a complete border on a table cloth whose perimeter is 1 meter long. Find the total length of the lace they both have bought. Will the lace be sufficient to cover the whole border?
Solution:
Length of lace bought by Geeta =
25 m
Length of lace bought by Shamim =
34 m
Total length of lace bought =
25 +
34LCM of 5 and 4 is 20.
25=
25×
44=
82034=
34×
55=
1520820+
1520=
2320=1
320This length is more than 1 m. So, lace is more than sufficient or will be left extra after covering the border.
7.9 Relation to Number Sequences Figure it Out (Page No. 181)
Question 1.
58−
38Solution:
Given
58−
38As fractional unit is same i.e.,
18 we shall simply subtract numerators keeping fractional unit as
18Then
58−
38=
5−38=
28=
14 (representing in simplest form)
Question 2.
79−
59Solution:
Given
79−
59As fractional unit is same i.e.,
19 we shall simply subtract numerators keeping fractional unit as
1979−
59=
7−59=
29Question 3.
1027−
1271027−
127Solution:
Here
1027−
127=
10−127=
927=
137.9 Relation to Number Sequences Figure it Out (Page No. 182)
Question 1.
Carry out the following subtractions using Brahmagupta’s method:
(a)
815−
315Solution:
Given
815−
315Fractional unit for both fractions is
115 then
815−
315=
8−315=
515=
13(b)
25−
415Solution:
Given
25−
415Here LCM of 5 and 15 is 15. Fractional unit for both fractions should be
115then
2×35×3−
4×115×1=
615−
415=
6−415=
215(c)
56−
49Solution:
Given
56−
49Hence LCM of 6 and 9 is 18. Fractional unit for both fractions should be
118 then
(d)
23−
12Solution:
Given
23−
12Here LCM of 3 and 2 is 6. Fractional unit for both fractions should be
16
Question 2.
Subtract as indicated:
(a)
134 from
103Solution:
The denominators of the given fractions are 3 and 4. The LCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
Then
134=
13×34×3=
3912,
103=
10×43×4=
4012Therefore,
103−
134=
4012−
3912=
112(b)
185 from
233Solution:
The denominators of the given fractions are 3 and 5.
The LCM of 3 and 5 is 15.
Then,
233=
23×53×5=
11515,
185=
18×35×3=
5415Therefore,
233−
185=
11515−
5415=
6115=4
115(c)
297 from
457Solution:
The denominators are same.
Therefore,
457−
297=
167=2
27Question 3.
Solve the following problems:
(a) Jaya’s school is
710 km from her home. She takes an auto for
12 km from her home daily, and then walks the remaining distance to reach her school. How much does she walk daily to reach the school?
Solution:
(a) Total distance between school and home =
710 km
Distance travelled in Auto =
12 km.
∴ Distance she walks daily to reach the school
(b) Jeevika takes
103 minutes to take a complete round of the park and her friend Namit takes
134 minutes to do the same. Who takes less time and by how much?
Solution:
Time taken by Jeevika =
103 minutes
and time taken by Narnit =
134 minutes
Now,
103×
44=
4012 and
134×
33=
3912Clearly,
103 >
134∴ Jeevika takes less ti me by
(
103−
134)
minutes
=
(
4012−
3912)
minutes
=
112 minutes.

![]()







![]()



![]()



![]()













![]()





![]()
![]()





![]()
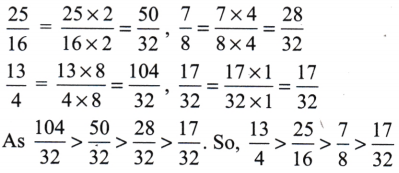
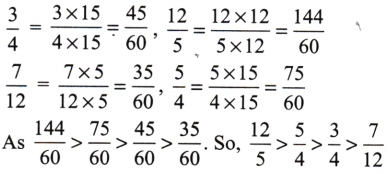
![]()
![]()
![]()


![]()







0 Comments