Science Class 7 Chapter 5 Question Answer Changes Around Us Physical and Chemical
Changes Around Us Physical and Chemical Class 7 Question Answer (InText)
Question 1.
(Page 57)
These students are describing some changes. What kinds of changes are they talking about?
Answer:
- Ice melts and becomes water. This is physical change as only state of water from solid to liquid has changed in this process.
- Bud blossoms to a flower, this is a chemical change as once a bud blooms into a flower, it cannot revert back to its bud form. Also, internal chemical changes takes place.
- Cold water becomes warm on keeping in open, this is a physical change as water remains the same, only its temperature changes.
- Rotting of banana is a chemical change as its composition and texture get changed.
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Question Answer Changes Around Us Physical and Chemical (Exercise)
Let Us Enhance Our Learning
Question 1.
Which of the following statements are the characteristics of a physical change?
(i) The state of the substance may or may not change.
(ii) A substance with different properties is formed.
(iii) No new substance is formed.
(iv) The substance undergoes a chemical reaction.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(c) (i) and (iii)
(i) The state of the substance may or may not change – Physical changes can involve changes in state (like melting or freezing) but no new substance is formed.
(iii) No new substance is formed – In a physical change, the substance remains the same, only its form or state changes.
Question 2.
Predict which of the following changes can be reversed and which cannot be reversed. If you are not sure, you may write that down. Why are you not sure about these?
(i) Stitching cloth to a shirt
Answer:
Stitching cloth to a shirt – Cannot be reversed: Once stitched, it is hard to undo without damage.
(ii) Twisting of straight string
Answer:
Twisting of straight string – Can be reversed: The string can be untwisted.
(iii) Making idlis from a batter
Answer:
Making idlis from a batter – Cannot be reversed: The batter cannot be returned to its original form after steaming.
(iv) Dissolving sugar in water
Answer:
Dissolving sugar in water – Can be reversed: Sugar can be recovered by evaporating water.
(v) Drawing water from a well
Answer:
Drawing water from a well – Can be reversed: Water can be returned to the well.
(vi) Ripening of fruits
Answer:
Ripening of fruits – Cannot be reversed: Once ripe, fruits cannot go back to unripe.
(vii) Boiling water in an open pan
Answer:
Boiling water in an open pan – Can be reversed: Evaporated water can be obtained back by condensation.
(viii) Rolling up a mat
Answer:
Rolling up a mat – Can be reversed: The mat can be unrolled.
(ix) Grinding wheat grains to flour
Answer:
Grinding wheat grains to flour – Cannot be reversed: Flour cannot be turned back into grains.
(x) Forming of soil from rocks
Answer:
Forming of soil from rocks – Cannot be reversed: Soil formation is a slow process and cannot form rock back.

Question 3.
State whether the following statements are True or False. In case a statement is False, write the correct statement.
1. Melting of wax is necessary for burning a candle. (True/False)
Answer:
True
2. Collecting water vapour by condensing involves a chemical change. (True/False)
Answer:
False: Collecting water vapour by condensing involves a physical change.
3. The process of converting leaves into compost is a chemical change. (True/False)
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Mixing baking soda with lemon juice is a chemical change. (True/False)
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks in the following statements:
(i) Nalini observed that the handle of her cycle has got brown deposits. The brown deposits are due to ______ and this
is a ______ change.
Answer:
rusting, chemical
(ii) Folding a handkerchief is a ______ change and can be ______ .
Answer:
physical, reversed
(iii) A chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen with evolution of heat is called ______, and this is a ______
change.
Answer:
combustion, chemical
(iv) Magnesium, when burnt in air, produces a substance called ______. The substance formed is ______ in nature. Burning of magnesium is a ______ change.
Answer:
magnesium oxide, basic, chemical
Question 5.
Are the changes of water to ice and water to steam, physical or chemical? Explain.
Answer:
Both, the change of water to ice and water to steam are physical changes. In both processes, the chemical composition of water remains the same; only its state changes from liquid to solid (ice) or from liquid to gas (steam). No new substance is formed which is a characteristic of physical changes.
Question 6.
Is curdling of milk a physical or chemical change? Justify your statement.
Answer:
The curdling of milk is a chemical change because, during this process, milk reacts with acid or bacteria, forming new substances like curd. This change cannot be reversed, which makes it a chemical change.
Question 7.
Natural factors, such as wind, rain, etc., help in the formation of soil from rocks. Is this change physical or chemical and why?
Answer:
The formation of soil from rocks involves both physical and chemical changes. Natural factors like wind, rain and temperature break down rocks into smaller pieces (physical change), while chemical processes, like weathering, also change the minerals in the rocks (chemical change). Both types of changes work together to form soil.

Question 8.
Read the following story titled ‘Eco-friendly Prithin’, and tick the most appropriate option(s) given in the brackets. Provide a suitable title of your choice for the story.
Prithvi is preparing a meal in the kitchen. He chops vegetables, peels potatoes, and cuts fruits (physical changes/chemical changes). He collects the seeds, fruits, and vegetable peels into a clay pot (physical change/ chemical change). The fruits, vegetable peels, and other materials begin to decompose due to the action of bacteria and fungi, forming compost (physical change/chemical change). He decides to plant seeds in the compost and water them regularly. After a few days, he notices that the seeds begin to germinate and small plants start to grow, eventually blooming into colourful flowers (physical change/chemical change). His efforts are appreciated by all his family members.
Answer:
Prithvi’s Green Kitchen
- Prithvi chops vegetables, peels potatoes, and cuts fruits – S physical changes
- He collects the seeds, fruits, and vegetable peels into a clay pot – V physical change
- He collects the seeds, fruits, and vegetable peels into a clay pot — V physical change
- The fruits, vegetable peels, and other materials decompose into compost — V chemical change
- Seeds germinate and grow into plants V chemical change
Question 9.
Some changes are given here. Write physical changes in the area marked ‘A’ and chemical changes in the area marked ‘B’. Enter the changes which are both physical and chemical in the area marked ‘C
Process of burning a candle; Tearing of paper; Rusting; Curdling of milk; Ripening of fruits; Melting of ice; Folding of clothes; Burning of magnesium and Mixing baking soda with vinegar.
Answer:
Question 10.
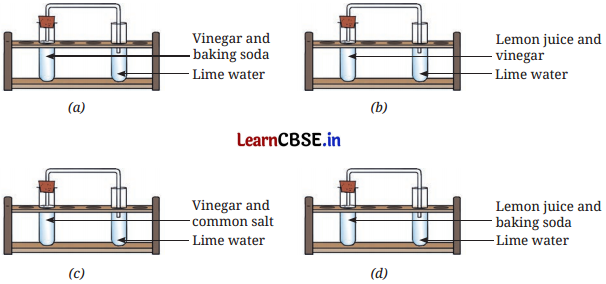
The experiments shown in Fig. 5.11a, b, c, and d were performed. Find out in which case(s) did lime water turn milky and why?
Answer:
In Figure (a), when vinegar reacts with baking soda, carbon dioxide gas is released. This carbon dioxide gas travels through the straw into the test tube with lime water, where it reacts to form calcium carbonate, a white solid substance that makes the lime water appear milky.
Class 7 Changes Around Us Physical and Chemical Question Answer (Activities)
Activity 5.1 Let Us Think and Reflect (Page 58)
| Change | Observation(s) |
| Melting ice cubes | Ice melts to water, state changes |
| Chopping vegetables | Size and shape changes |
| Boiling water | Water changes to water vapour, state changes |
| Making popcorn from corn | Corns get roasted into bigger size popcorns (new substance formed), shape and size changes |
| Cutting a piece of paper | Shape and size changes |
| Adding beetroot extract to water | Colour of water changes to pink |
| Burning wood | Wood changes to ash (new substance formed), heat and light produced |
| Drying wet clothes | Water from wet clothes gets evaporated, state of water changes from liquid to gas |
| Making small balls of dough | Shape and size changes |
| Rolling small balls of dough into chapatis | Shape and size changes |
| Cooking of food | Composition, smell and taste changes |
| Making pot from mud | Shape and size changes |
Conclusion: We can categorise these changes in two types of changes, one in which only shape, size or state of a substance changes or other in which new substance(s) is/ are formed.
Activity 5.2: Let Us Create and Discuss (Page 59)
Changes listed in A, B and C are as follows:
A. Creating some objects with paper: When we create different objects like aeroplane, boat, bird, etc. by folding a sheet of paper, only shape and size changes. We can get back the original sheet by unfolding it again.
B. Playing with a balloon: When we loosen the grip of the inflated balloon we get the original shape of balloon back, and we can inflate it again but when we prick the inflated balloon with a pin, it gets deflated with a hole in it, so we cannot able to inflate it again.
C. Crushing a piece of chalk: When we crushed a piece of chalk to powder form, we cannot can get back the original piece of a chalk.
Observation and conclusion: In all these types of changes, material (piece of paper, balloon, chalk) remains the same but their size and shape changes only. Thus, these are examples of physical changes.
Activity 5.3: Let Us Create and Discuss (Page 60)

Observation and conclusion: When we blow air (carbon dioxide) from mouth to tumbler A containing water, we do not observe any change in the colour of water. But when we blow air into tumbler B containing lime water (calcium hydroxide), lime water turns milky and white-coloured insoluble substance (calcium carbonate) gets settle down. Thus, this is classified as chemical change as new substance is being formed.

Activity 5.4: Let Us Experiment (Page 61)
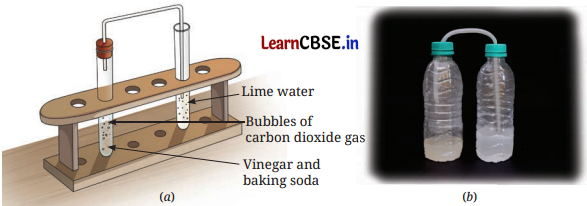
Observation and conclusion: When we add a pinch of baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) to vinegar or lemon juice, bubbles of carbon dioxide gas are produced with a fizzing sound. When we pass this gas to lime water, it turns milky. Thus, in this process, new substances are formed, it is a chemical change.

Activity 5.5: Let Us Investigate (Pages 62-63)

Observation and conclusion: In figure (a), candle keeps on burning as it is not covered and supply of air (oxygen) is available. But in figure (b), as candle is covered with a glass tumbler, does not get a continuous supply of air, so, it gets extinguished. This concludes oxygen is required for combustion.
Activity 5.6: Let Us Investigate (Page 64)

Observation and conclusion: The substance catches fire only when its ignition temperature is reached. Ignition temperature is the minimum temperature at which the substance catches fire. When a lighted matchstick is brought near to the paper it catches fire immediately because the temperature of the matchstick is already higher that the ignition temperature of the paper. In another case, when sunrays are focused using a magnifying glass on a piece of paper, it gets heated up and the temperature of paper increases and it attains its ignition temperature and starts burning and emit smoke.
Requirements for combustion process to occur:
- A combustible substance (fuel)
- Oxygen
- Attainment of ignition temperature.

Activity 5.7: Think, Pair, and Share (Page 65)

Conclusion: Burning of a candle involves both physical and chemical change. Melting of wax, evaporation of wax to wax vapour and solidification of melted wax to solid wax are all physical changes. While burning of wax to produce new substance, carbon dioxide is a chemical change.
Activity 5.8: Let Us Think (Page 66)
Table 5.2; Can changes be reversed?
| Change | The original state can be brought back (Yes/ No) |
| Melting ice cubes | Yes |
| Chopping vegetables | No |
| Boiling water | Yes |
| Making popcorn from corn | No |
| Cutting a piece of paper | No |
| Adding beetroot extract to water | No |
| Burning wood | No |
| Diying wet clothes | Yes |
| Making small balls of dough | Yes |
| Rolling small balls of dough into chapatis | Yes |
| Cooking of food | No |
| Making pot from mud | No |
Conclusion: Changes around us can be grouped into reversible (original substance can be brought back) and irreversible (original substance cannot be brought back) changes.

![]()
![]()






![]()


![]()







0 Comments